Eyelid retraction
What is eyelid retraction?
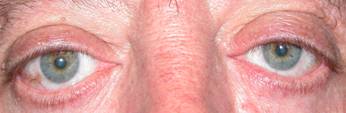
Normally the upper eyelid should cover about two millimeters of the cornea and the lower eyelid should get right to the limbus (border between cornea and sclera).
Any upward modification of the upper eyelid up or downward modification of the lower eyelid retraction is considered retraction.
What are its causes?
Its causes are many:
- Variations of normal anatomy causing small cheek bones and large orbits.
 |
- Aging
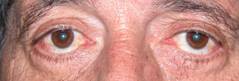 |
- High degree of myopia
 |
- Thyroid disease affecting the orbit
 |
- Radiotherapy
 |
- Tumours
- Inflammation
What are the symptoms?
Due to increased corneal exposure, patients may complain of dry eye symptoms, irritation, redness, tearing, blurred vision and irritation.
How is it treated?
Treatment always involves surgery of the lower eyelid. In the upper eyelid can make temporary descents can be achieved with Botox, that way the levator paralyzed upper eyelid ptosis produces temporary elevation, which lasts approximately 6 months.
In cases of moderate upper eyelid retraction do mullerectomy is performed (removing a small muscle whose function is to elevate the eyelid). That way the upper eyelid can drop one or two millimeters. If retraction is more pronounced we can produce partial ptosis, lengthening or weakening the upper eyelid levator. In more severe cases we put spacers to increase its length.
In mullerectomy stitches are not necessary and access is internal.
 |
 |
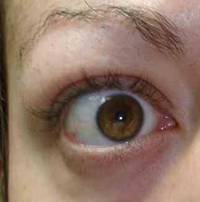 |
| Mullerectomy. Before-after | ||
In the lower eyelid
If the retraction is slight, cantoplasty may be used, tarsal side strips employing the same technique as in ectropion, and thereby raising the lid to adjust its lateral angle.
In more severe cases spacers are employed, as well as biological grafts such as sclera, ear cartilage, or palate.
 |
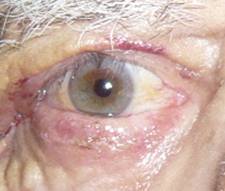 |
| Lower eyelid retraction. Correction auricular cartilage graft | |
 |
 |
| Lower eyelid retraction. Correction with donor sclera grafts.Before-after |
 |
 |
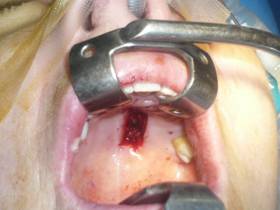
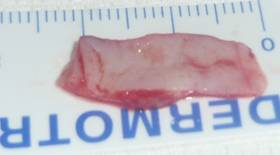
| Correction of lower eyelid retraction with hard palate graft. Before-after |
|
 |
|
 |
|
| Hard palate graft | |
In very particular cases of recurrent facial hemilateral paralysis we lift the middle third of the face, i.e. raising the cheek to anchor it more superiorly and from there changing the height of the eyelid.









