Xanthelasma
What is xanthelasma?
They are benign lesions appearing as yellowish plaques that appear most frequently on the eyelids in the area surrounding the tear duct, both in the upper lid and in the bottom. They may occur in both eyes at once. These lesions are located in the skin layer and do not involve the orbit.
 |
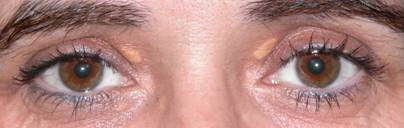 |
| Xanthelasmas in upper eyelids |
There are other injuries, within the broad spectrum of xanthelasma (xanthogranulomatosis), most important, considering as tumors affecting the eyelids fat conferring a woody stiff consistency. This disease is rarer. The oculoplastic specialist to determine what kind of injury is and the best treatment.
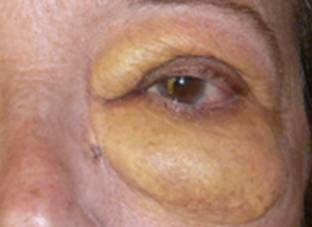 |
| Xanthogranulomatosis |
What causes xanthelasmas?
Xanthelasmas are deposits of fat and cholesterol, which are sometimes linked to serum cholesterol levels or metabolic disorders but frequently appear in absence of them.
Therefore they may occur in isolation. They have a special predilection for the medial palpebral location (near the nose).
Xanthogranulomatosis are diseases that affect eyelid and orbital fat pouches. They may be associated with other major diseases. They are very rare compared to the frequency of xanthelasmas.
What are the symptoms?
Generally they are asymptomatic causing merely cosmetic concerns in the case of xanthelasmas.
In the event that injuries correspond to diseases of another spectrum (xanthomatosis, xanthogranulomatosis) clinical presentation is different and usually consists of an increase of the orbital fat pads, which produce increased eyelid bags which can sometimes be very noticeable.
How is xanthelasma treated?
There are many forms of treatment.
Surgery: is the most common treatment due to location and depth of the lesions. It is easier if they appear in the upper eyelid where the scars can be hidden and habitual excess skin in the area allows the absence of complications.
In the lower eyelid we must be more careful because less skin is available here, the scar is more visually exponed, and postoperative retractions may occur.
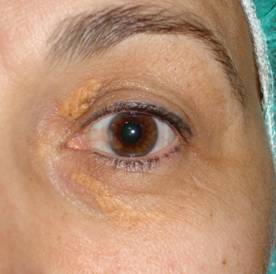 |
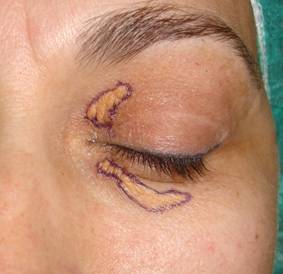 |
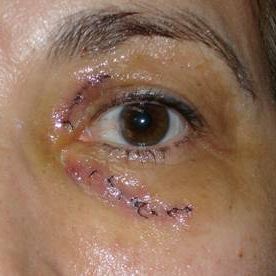 |
|
Xanthelasmas postoperative surgery to 24 hours. |
|
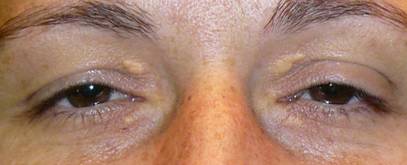 |
| BEFORE |
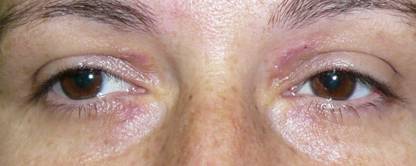 |
| AFTER |
| Postoperative xanthelasmas surgery at 7 days |
Peeling with trichloroacetic acid and CO2 laser, producing a superficial burn that can leave hypopigmented skin.
Nd laser: YAG: produces less scarring.
Xanthelasmas often produce much thickening of the skin that causes the laser to be ineffective. Surgery remains the only solution in these cases.
Surgery is performed under local anesthesia. The running time is 15 minutes short by injury. It must employ sutures that are removed at one week.
Depending on the degree of extension it is not always possible in a first surgery to remove the entire lesion. Similarly, the form of the xanthelasma influences the type of surgery. Skin grafos may even be necessary.
Recovery time after surgery is short.
Xanthelasma may reappear even even after being completely eradicated.
Your surgeon will explain proper postoperative care.









